Post-mortem approach
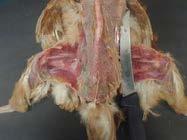
1. Pluck the feathers from the dorsum and ventrum
2. Disarticulate the leg
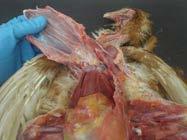
3. Expose the pectoral muscle
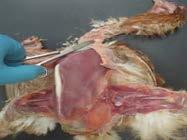
Reflect or remove the coelomic skin cranially over the sternum and up to the neck to the intermandibular space.
4. Visualise the air sacs while removing keel/pectoral muscle
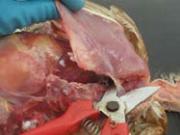
Cut the ribs from the lateral chest and the clavicle and coracoids bones at the thoracic inlet. Lift the keel and pectoral muscles to expose the air sacs. Check the air sacs – they should be clear/cling film like. Opacity in the air sacs may be airsacculitis.
5. Remove the sternum
6. Reflect the coelomic musculature
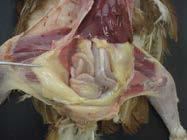
Reveal the gastrointestinal tract. If fibrinous exudate is present in the coelom or air sacs, a swab should be placed into bacterial transport media.
7. Visualise the bursa in dorsal cloacal wall
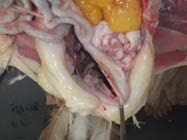
Reflect the ventriculus cranially and to the right. Visualise the bursa/remnant by moving distal colon to the right. The bursa will have regressed in sexually mature birds. Fixed bursa should be taken in younger birds.
8. Remove the heart

Remove the heart at base (collect a fixed and fresh sample). Examine the dorsal air sacs once the heart is removed.