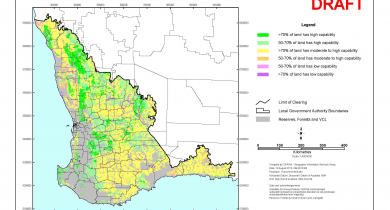
Land use
Western Australia is the largest Australian State, spanning 2 400 kilometres from north to south, and experiencing a variety of climatic conditions, soil and land properties, and water availability. Accordingly, the state is suited to a variety of agricultural industries ranging from open range grazing and broadacre cereal cropping through to irrigated pastures and horticulture, orchards and vineyards.
The Department of Agriculture and Food, Western Australia provides the advice, support and tools needed to ensure the State’s land has the capability to sustain agricultural use, without degrading the soil and water resources on which it relies, and to ensure our most valuable agricultural land is protected from non-agricultural development.
Articles
Filter by search
Filter by topic
- (-) Remove Water filter Water
- Crops (6) Apply Crops filter
- Resource assessment (6) Apply Resource assessment filter
- (-) Remove Managing soils filter Managing soils
- (-) Remove Soils filter Soils
- Soil salinity (5) Apply Soil salinity filter
- Pastures (1) Apply Pastures filter
- Report card on conditions and trends (1) Apply Report card on conditions and trends filter
- Water management (1) Apply Water management filter
- New horticulture crops (1) Apply New horticulture crops filter
- Assessment for agricultural expansion (1) Apply Assessment for agricultural expansion filter
- Horticulture (1) Apply Horticulture filter
- Irrigated crops (1) Apply Irrigated crops filter
- Measuring and assessing soils (1) Apply Measuring and assessing soils filter